BRUKINSA patients can call the myBeOne Support™ program to talk to a dedicated nurse: 1-833-234-4363
BRUKINSA works to help you take control of your
- BRUKINSA has been shown to block 100% of BTK in blood cells and 94% to 100% of BTK in lymph nodes when taken at the recommended total daily dose of 320 mg. The significance of blocking up to 100% of BTK on treatment responses has not been established
- Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a protein that signals to cancerous B cells (like those that cause CLL or SLL), helping them to grow and spread
- Blocking BTK can help stop this signaling
A diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) can be difficult and overwhelming. That’s why it is important to discuss the benefits and risks of treatment options and responses with your doctor.
In the BRUKINSA trials, 2 types of responses were studied. Progression-free survival (PFS), or the rate at which patients live without their disease worsening, was 1 response and the main purpose of this study. The other response, and a secondary purpose of this study, was overall response rate (ORR), or the percentage of patients in which treatment is working.
Talking to your doctor about these responses can help you find the treatment option that may be right for you.
In a trial comparing BRUKINSA to a combination therapy known as BR, more patients taking BRUKINSA continued responding to treatment with no sign of CLL/SLL worseningThe trial included 589 patients who had never received treatment for their CLL/SLL. 479 patients in the trial who did not have a genetic mutation known as del(17p) received either BRUKINSA or BR, which is a combination of bendamustine (a type of chemotherapy) and rituximab (a targeted therapy). There were also 110 patients with the del(17p) mutation who received BRUKINSA in a separate treatment arm.

- 58% relative reduction in the risk of CLL/SLL worsening for patients taking BRUKINSA compared to those taking BR
*When patients improved, tests showed that their cancer got smaller in size and did not spread.
Patients with the del(17p) mutation responded to treatment with BRUKINSACertain people with CLL/SLL have a genetic mutation called del(17p). Because these patients don’t usually respond well to chemoimmunotherapy, they were studied separately to see how they’d respond to just BRUKINSA.
2-Year Progression-Free Survival: with del(17p)
89
(110 BRUKINSA patients)
Individual results may vary.
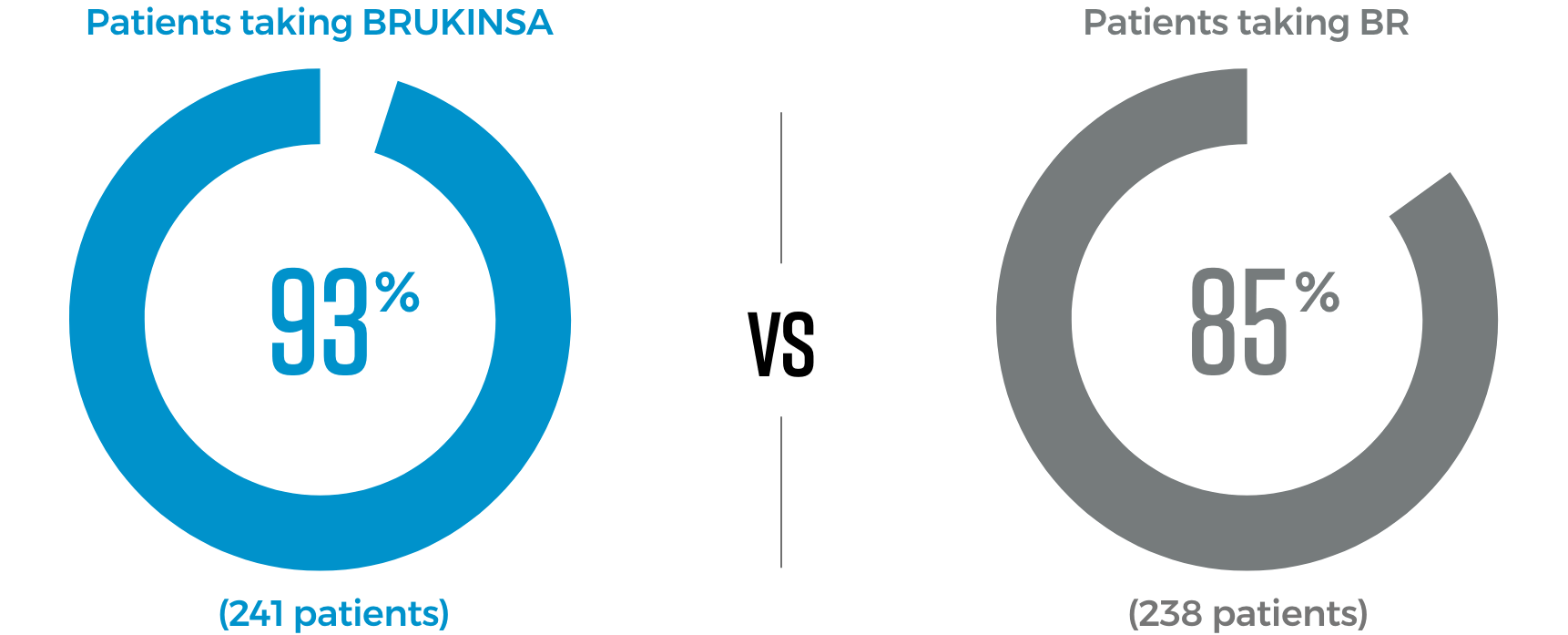
Fewer patients stopped treatment with BRUKINSA because of side effects than those taking BR

This BRUKINSA-only study included CLL/SLL patients, some of whom received BRUKINSA as their first treatment and some of whom received BRUKINSA after receiving a prior treatment.
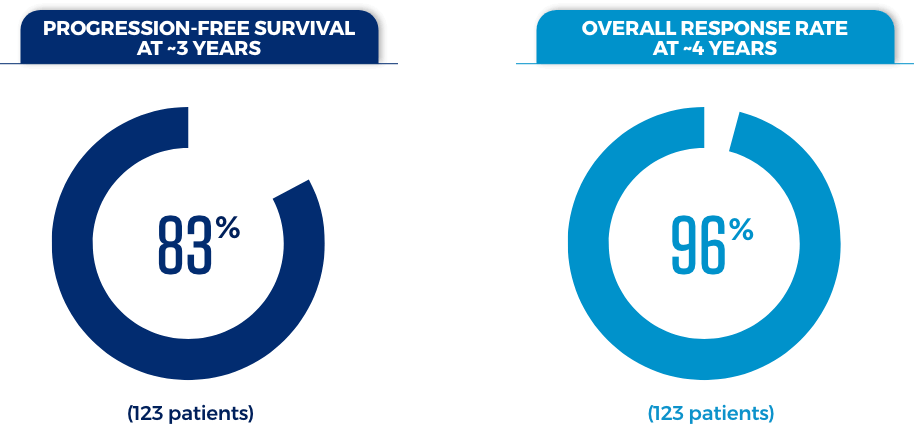
These results presented are consistent with, but not included in, the FDA-approved prescribing information.
Individual results may vary.
People taking BRUKINSA may experience side effects. In CLL/SLL clinical trials, 8% of previously untreated and 15% of previously treated patients discontinued treatment due to side effects. It’s important to remember that everyone responds to medication differently.
Speak to your doctor about side effects of concern. Most side effects can be managed by your doctor to help you feel better and stay on treatment. Be sure to tell your doctor right away about any new or worsening side effects.
The most common side effects of BRUKINSA include:- Decreased white blood cell count
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Decreased platelet count
- Bleeding
- Muscle, bone, or joint pain
- Bleeding problems (hemorrhage). Bleeding problems are common with BRUKINSA, and can be serious and may lead to death. Your risk of bleeding may increase if you are also taking a blood thinner medicine. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of bleeding, including:
- blood in your stools or black stools (looks like tar)
- pink or brown urine
- unexpected bleeding, or bleeding that is severe or you cannot control
- vomit blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- cough up blood or blood clots
- increased bruising
- dizziness
- weakness
- confusion
- change in speech
- headache that lasts a long time
- Infections that can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have fever, chills, or flu-like symptoms.
- Decrease in blood cell counts (white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells). Your healthcare provider should do blood tests during treatment with BRUKINSA to check your blood counts.
- Second primary cancers. New cancers have happened in people during treatment with BRUKINSA, including cancers of the skin or other organs. Use sun protection when you are outside in sunlight.
- Heart rhythm problems (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular arrhythmias) that can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following signs or symptoms:
- your heartbeat is fast or irregular
- feel lightheaded or dizzy
- pass out (faint)
- shortness of breath
- chest discomfort
- Liver problems. Liver problems, which may be severe or life-threatening, or lead to death, can happen in people treated with BRUKINSA. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver before and during treatment with BRUKINSA. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have any signs of liver problems, including stomach pain or discomfort, dark-colored urine, or yellow skin and eyes.
These are not all the possible side effects of BRUKINSA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
If side effects occur, partnering with your doctor can help you manage any symptoms you may experience and may help ensure you can continue treatment with BRUKINSA.
You will continue to take BRUKINSA for as long as your doctor thinks it is helping you, or for as long as side effects are manageable.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking BRUKINSA?
Before taking BRUKINSA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have bleeding problems.
- have had recent surgery or plan to have surgery. Your healthcare provider may stop BRUKINSA for any planned medical, surgical, or dental procedure.
- have an infection.
- have or had heart rhythm problems.
- have high blood pressure.
- have liver problems, including a history of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. BRUKINSA can harm your unborn baby. If you are able to become pregnant, your healthcare provider may do a pregnancy test before starting treatment with BRUKINSA.
- Females should avoid getting pregnant during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA. You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA.
- Males should avoid getting female partners pregnant during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA. You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if BRUKINSA passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with BRUKINSA and for 2 weeks after the last dose of BRUKINSA.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Taking BRUKINSA with certain other medications may affect how BRUKINSA works and can cause side effects.
What are the possible side effects of BRUKINSA?
BRUKINSA may cause serious side effects, including:
- Bleeding problems (hemorrhage). Bleeding problems are common with BRUKINSA, and can be serious and may lead to death. Your risk of bleeding may increase if you are also taking a blood thinner medicine. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of bleeding, including:
- blood in your stools or black stools (looks like tar)
- pink or brown urine
- unexpected bleeding, or bleeding that is severe or you cannot control
- vomit blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- cough up blood or blood clots
- increased bruising
- dizziness
- weakness
- confusion
- change in speech
- headache that lasts a long time
- Infections that can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have fever, chills, or flu-like symptoms.
- Decrease in blood cell counts (white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells). Your healthcare provider should do blood tests during treatment with BRUKINSA to check your blood counts.
- Second primary cancers. New cancers have happened in people during treatment with BRUKINSA, including cancers of the skin or other organs. Your healthcare provider will check you for other cancers during treatment with BRUKINSA. Use sun protection when you are outside in sunlight.
- Heart rhythm problems (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular arrhythmias) that can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following signs or symptoms:
- your heartbeat is fast or irregular
- feel lightheaded or dizzy
- pass out (faint)
- shortness of breath
- chest discomfort
- Liver problems. Liver problems, which may be severe or life-threatening, or lead to death, can happen in people treated with BRUKINSA. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver before and during treatment with BRUKINSA. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have any signs of liver problems, including stomach pain or discomfort, dark-colored urine, or yellow skin and eyes.
The most common side effects of BRUKINSA include:
- decreased white blood cell count
- decreased platelet count
- upper respiratory tract infection
- bleeding
- muscle, bone, or joint pain
These are not all the possible side effects of BRUKINSA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What is BRUKINSA?
BRUKINSA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with:
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL).
- Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
- Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior treatment for their cancer.
- Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) when the disease has come back or did not respond to treatment and who have received at least one certain type of treatment.
- Follicular lymphoma (FL), in combination with the medicine obinutuzumab, when the disease has come back or did not respond to treatment and who have received at least two prior treatments.
It is not known if BRUKINSA is safe and effective in children.
Please see full Prescribing Information including Patient Information.

